COPD
Enhance Lung Capacity and Ease Breathing with Yoga for COPD
COPD is a group of lung diseases that make breathing difficult. The two main types are emphysema and chronic bronchitis. Emphysema damages the air sacs in your lungs, making it harder to take in air. Chronic bronchitis causes inflammation and mucus buildup in the airways, making it difficult to breathe out.
- Smoking: The leading cause of COPD, smoking damages the lungs and airways over time.
- Exposure to secondhand smoke: Inhaling secondhand smoke can contribute to developing COPD, even if you never smoked yourself.
- Air pollution: Long-term exposure to air pollution can irritate the lungs and contribute to COPD development.
- Occupational dust and fumes: Exposure to dust and fumes in certain workplaces can increase the risk of COPD.
- Genetics: Some people are genetically predisposed to developing COPD, especially if they have a family history of the disease.
- Lung and airway damage: Primarily caused by long-term exposure to irritants, like cigarette smoke, that damage lung tissue and airways.
- Other potential contributors: In rare cases, long-term exposure to air pollution, occupational dusts and chemicals, or childhood respiratory infections can also contribute.
- Breathlessness: Shortness of breath, especially when active, climbing stairs, or talking.
- Wheezing: A whistling sound during breathing, indicating narrowed airways.
- Chest tightness: Feeling of discomfort or pressure in the chest.
- Productive cough: A cough that brings up mucus, often phlegm-like.
- Frequent infections: Increased susceptibility to chest colds, bronchitis, and pneumonia.
- Fatigue and tiredness: Feeling drained and lacking energy due to impaired oxygen intake.
- Ankle, foot, or leg swelling: This can occur in advanced stages due to fluid buildup in the body.
- Savasana (Corpse Pose): Promotes deep relaxation and controlled breathing, which can help reduce stress and improve lung function in individuals with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD). It encourages mindfulness and gentle awareness of breath, aiding in respiratory relaxation.
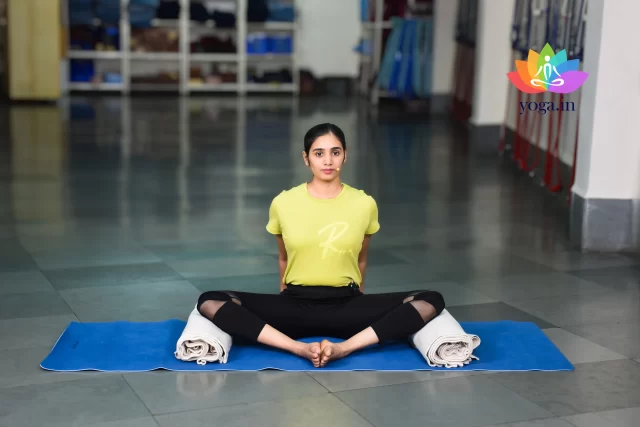
- Supta Baddha Konasana (Gracious Pose): Helps open the chest and improve lung capacity, making it beneficial for individuals with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD). It promotes deep, relaxed breathing, easing tension in the chest and encouraging better airflow.
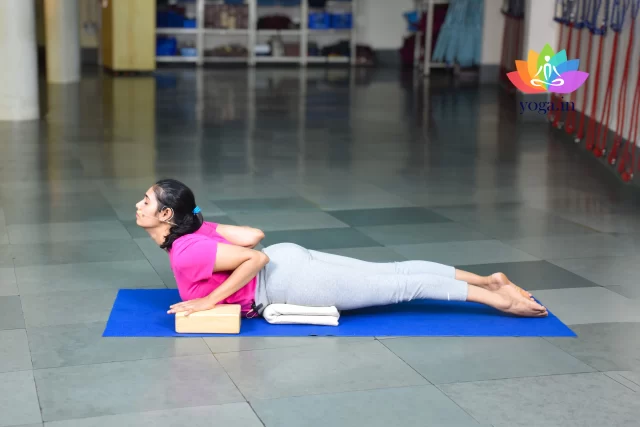
- Purvottanasana (Upward Plank Pose): Opens the chest and shoulders, promoting better lung expansion and deeper breathing, which can be beneficial for individuals with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD). It helps improve posture, increase lung capacity, and encourage respiratory health.
- Upvista Konasana (Wide-Angled Seated Forward Bend): Opens the chest and encourages deep breathing, which can help individuals with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) improve lung capacity. It stretches the spine and promotes better airflow, supporting respiratory health.
- Baddha Konasana (Bound Angle Pose): Opens the chest and promotes deeper breathing, which can aid individuals with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) in improving lung function. It also helps reduce tension in the body and encourages relaxation, supporting overall respiratory health.
- Bhujangasana (Cobra Pose): Gently stretches the chest and strengthens the back muscles.
- Shalabhasana (Locust Pose): Strengthens the back muscles and improves lung capacity.
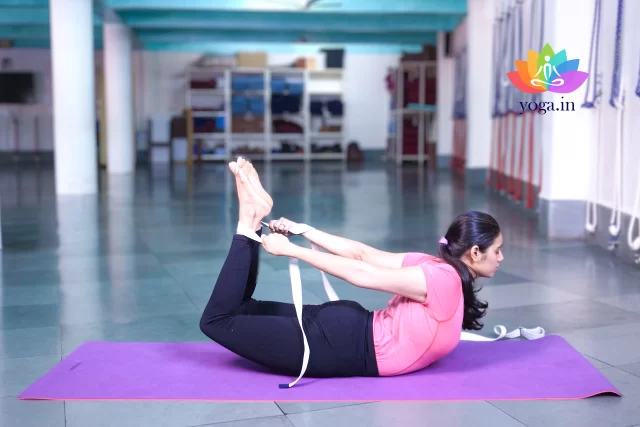
- Dhanurasana (Bow Pose): Opens the chest and strengthens the back muscles.
- Ushtrasana (Camel Pose): Opens the chest and improves breathing.
- Setubandha Sarvangasana (Bridge Pose): Opens the chest and improves lung expansion, which can help individuals with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) breathe more deeply. The pose also strengthens the back and encourages better posture, aiding in overall respiratory function.
- Kapalbhati Pranayama (Skull-Shining Breath): This energizing breath technique helps clear mucus and improve lung capacity.
- Bhastrika Pranayama (Bellows Breath): This faster-paced breathing technique can help strengthen respiratory muscles and improve lung function.
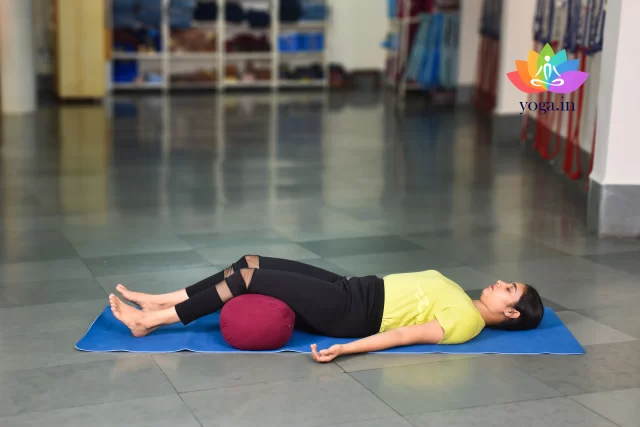
Savasana
शवासना / Corpse pose
The sanskrit name is derived from Śava (शव) meaning "corpse" and āsana (आसन) …
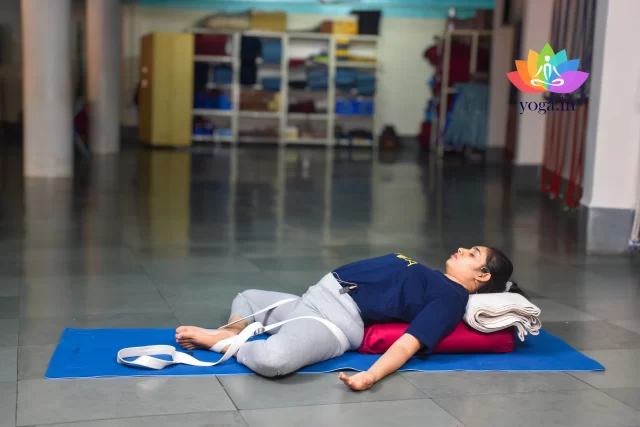
Supta Baddha Konasana
सुप्त बधकोनासन / Gracious pose
The Sanskrit name is derived from supta, which means “reclining,” baddha, which …
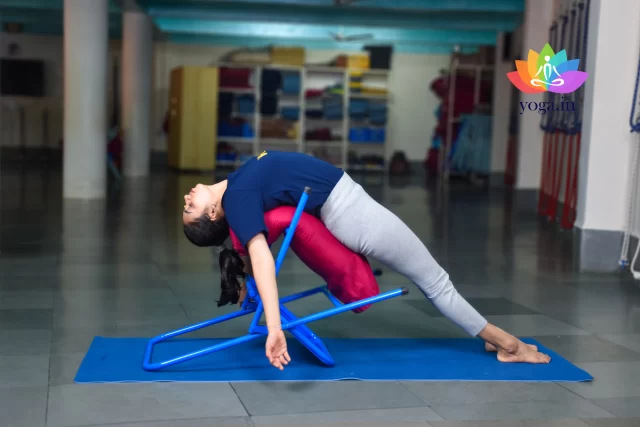
Purvottanasana
पूर्वोतानासन / Upward Plank Pose
Purvottanasana, or Reverse Plank Pose, translates to "Intense East Stretch Pose" …
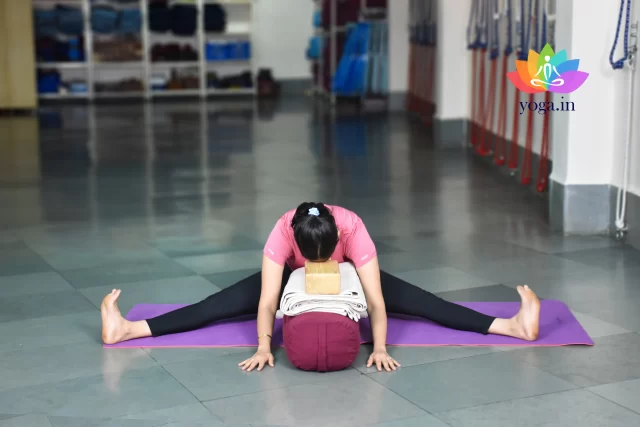
Upvishta konasana
उपविष्टा कोणासन / Wide-Angled Seated Forward Bend
The Sanskrit name is derived from Upavistha (उपविष्टा) means open/seated, Kona …
Baddha konasana
बद्ध कोनासन / Bound angle pose
The sanskrit name is derived from Baddha ( बद्ध) ,meaning "bound", Koṇa (कोण) …
Bhujangasana
भुजंगासन / Cobra Pose
The Sanskrit name is derived from bhujanga (भुजंगा) meaning cobra or snake and āsana (आसन) …
Shalabhasana
शलभासन / Locust pose
The Sanskrit name is derived from Salabha (शलभा) meaning locust and āsana (आसन) …
Dhanurasana
धनुरासन / Bow Pose
The Sanskrit name is derived from Dhanur (धनुर) means bow and āsana (आसन) meaning …
Ushtrasana
उष्ट्रासनI / Camel pose
The name is derived from Ushtra (उष्ट्रासनI) meaning camel and Asana (आसन) meaning …
Setubandha Sarvangasana
सेतुबन्ध सर्वंगासन / Bridge pose
The Sanskrit name is derived from Setu (सेतु) meaning bridge, Bandha (बन्धा) …
Kapalbhati Pranayama
कपालभाति प्राणायाम / Skull Shining Breath
"Kapalbhati" comes from "Kapala," meaning "skull," and "Bhati," meaning "shining" …
Bhastrika Pranayama
भस्त्रिका प्राणायाम / Bellows Breath
The Sanskrit word “Bhastrika” means “bellows”, Prana meaning “Life force energy,” …