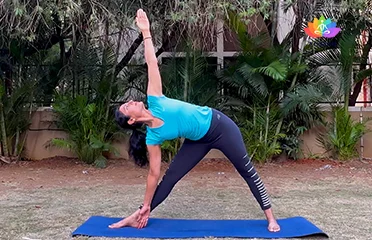Marichyasana (Sage Twist Pose)
मरीच्यासन / Sage Twist Pose
The Sanskrit name is derived from Marichya (मरीच्) meaning ray of [�K]
Naukasana (Boat Pose)
नौकासन / Boat Pose
The Sanskrit name is derived from Nava ( नाव) meaning boat and asana (आसन) [�K]
Parsvakonasana (Extended Lateral Angle P
पार्श्वकोनासन / Extended Lateral Angle Pose
The Sanskrit name is derived from Parsva (पार्श्व) meaning side, [�K]
Parsvottanasana (Intense Side Stretch Po
पार्श्वोत्तनासनम् / Intense Side Stretch Pose
The Sanskrit name is derived from parsva (पार्श्वो) meaning [�K]
Paschimottanasana (Seated Forward Bend)
पश्चिमोत्तानासन / Seated Forward Bend
The Sanskrit name is derived from three sanskrit words: Paschima (पश्चिमा) [�K]
Shalabhasana (Locust Pose)
सलभासन / Locust Pose
The Sanskrit name is derived from Shalabha (शलभा) meaning locust and [�K]
Sirsasana (Headstand)
शीर्षासन / Headstand
The Sanskrit name is derived from Sirsa (शीर्ष) meaning head and asana [�K]
Tadasana (Mountain Pose)
ताड़ासन / Mountain Pose
The sanskrit name is derived from tada (ताड़ा) meaning mountain and [�K]
Trikonasana (Triangle Pose)
त्रिकोणासन / Triangle Pose
The sanskrit name is derived from three Sanskrit Words: Tri (त्रि) meaning [�K]
Upavishta Konasana (Wide-Angled Seated F
उपविष्ट कोनासन / Wide-Angled Seated Forward Bend
The Sanskrit name is derived from Upavistha (उपविष्ट) means open/seated, [�K]
- 1
- 2
- 3
Finding Ease within: Yoga and Pranayama for Bloating
“Yoga is the journey of the self, to the self, through the self.” – B.K.S. Iyengar
What is Bloating?
Bloating is a common digestive discomfort characterized by a feeling of tightness or fullness in the abdomen. It can be caused by excess gas, fluid retention, or digestive issues. While typically harmless, bloating can be quite uncomfortable and lead to social anxiety or a reluctance to participate in certain activities.
Symptoms of Bloating
- Abdominal distention: A feeling of tightness or fullness in the abdomen
- Visible swelling of the abdomen
- Excessive gas
- Burping
- Abdominal pain or cramping
- Feeling of pressure or tightness in the clothing around the abdomen
Causes of Bloating
Several factors can contribute to bloating, including:
- Gas: Gas buildup in the intestines can cause significant distention and discomfort. This can be caused by swallowing air while eating or drinking, consuming certain gas-producing foods (beans, cruciferous vegetables), or bacterial fermentation in the gut.
- Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS): IBS is a chronic condition characterized by abdominal pain, cramping, bloating, and diarrhea or constipation. The exact cause of IBS is unknown, but stress, diet, and gut bacteria are thought to play a role.
- Constipation: When stool remains in the colon for too long, it can lead to bloating and discomfort.
- Food Intolerances: Intolerances to certain foods, such as lactose (dairy) or gluten (wheat), can cause bloating as the body struggles to digest them properly.
- Hormonal fluctuations: Women may experience bloating due to hormonal changes during their menstrual cycle or pregnancy.
Treatment of Bloating through Yoga and Pranayama
Yoga and Pranayama offer a natural approach to managing bloating alongside any dietary or medical treatment plans. Yoga postures (asanas) can help massage the digestive organs, stimulate circulation, and ease discomfort. Pranayama (breathing exercises) can promote relaxation and reduce stress, which may worsen bloating.
Diet for Bloating
- Include anti-inflammatory foods: Fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and fatty fish rich in omega-3s can help reduce inflammation and promote gut health.
- Stay hydrated: Drinking plenty of water keeps your digestive system functioning optimally and may help reduce bloating.
- Limit processed foods: Sugary drinks, processed meats, and refined carbohydrates can contribute to inflammation and bloating.
- Identify and limit food triggers: Pay attention to foods that worsen your bloating and limit or eliminate them from your diet. This may include dairy, gluten, or certain fruits and vegetables.
- Maintain a healthy weight: Excess weight can put strain on the digestive system and contribute to bloating.
Caution for Bloating
- Listen to your body: Respect your limits and avoid poses that cause pain or discomfort.
- Modify or skip poses: If a pose feels uncomfortable, adapt it or skip it altogether. There are many variations of yoga postures to suit different abilities.
- Seek guidance: Consider working with a qualified yoga therapist or teacher experienced in digestive issues for personalized support.
- Disclose medical history: Inform your yoga teacher about any pre-existing medical conditions or digestive issues to ensure a safe practice.
Contraindications (Who Should Not Do It)
- Acute abdominal pain: Avoid yoga if you are experiencing sudden or severe abdominal pain. Consult a doctor immediately.
- Hiatal hernia: Certain yoga poses may worsen hiatal hernia symptoms. Discuss with your doctor and yoga teacher for safe modifications.